A radial velocity study of the cataclysmic variable LAMOST J035913.61+405035.0
This research project used data taken from the Intermediate Dispersion Spectrograph (IDS) instrument on the 2.5-m Isaac Newton Telescope (INT) in La Palma. Data were taken, reduced and analysed during the 2023/24 academic year. A cataclysmic variable (CV) is a type of interacting binary system where a white dwarf primary star accretes mass from a late-type secondary star which fills its Roche-lobe. Their evolution is driven by the loss of angular momentum, which drives the stars closer together at shorter orbital periods.
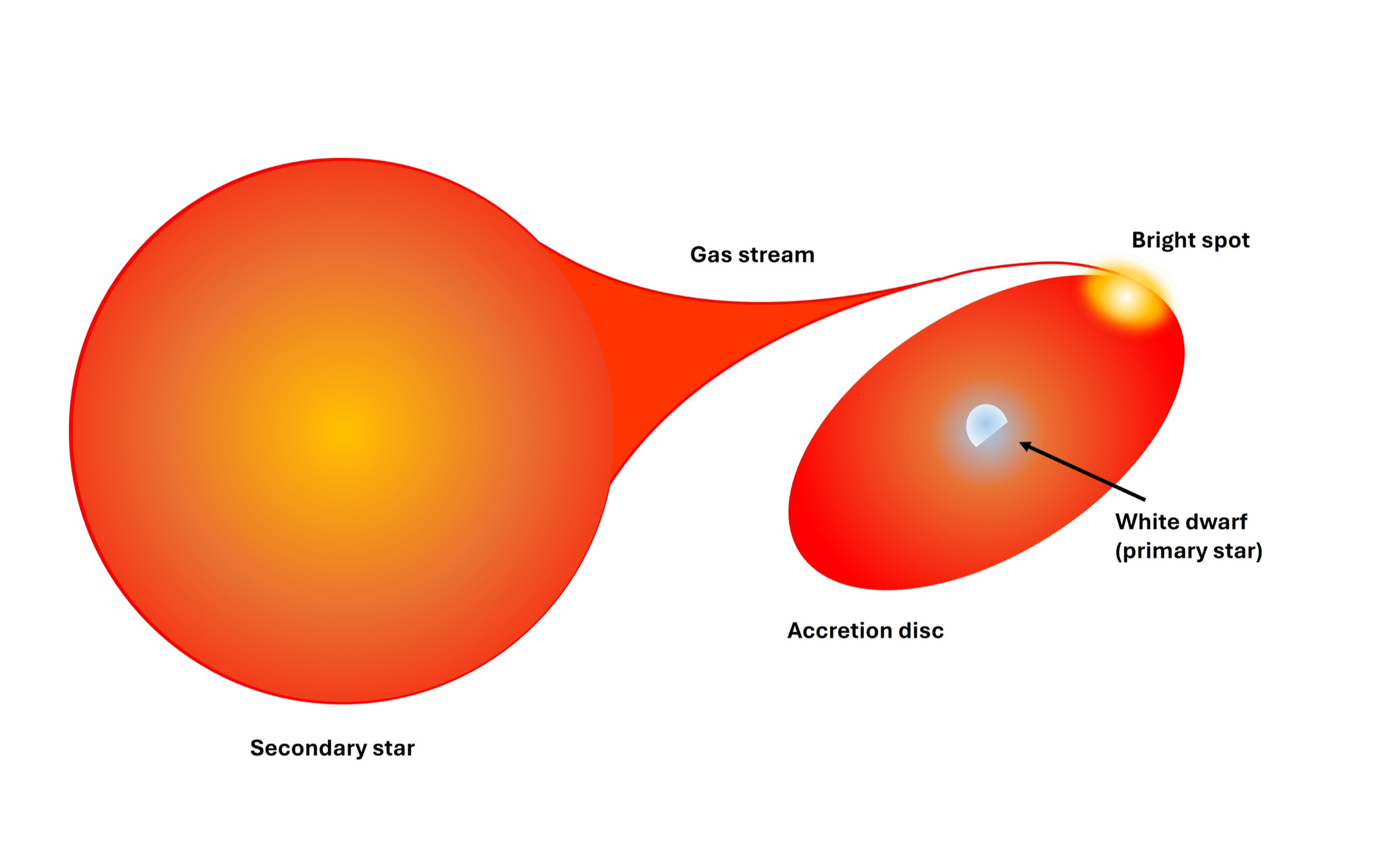
The masses of the primary and secondary stars in a CV dominate the systems properties. Mass determinations can be done from photometric observations of CVs, by modelling the lightcurves. This photometric technique has been shown to be accurate for many systems, but relies on several assumptions. These models are tested by comparing independent mass measurements with the photometric values. The aim of this research was to measure the component masses of the CV LAMOST J035913.61+405035.0 by determining the radial velocity of the secondary star using spectroscopic measurements.
Dissertation below: